Our competitive world brings additional challenges for students. Finding a decent job, an internship, or a scholarship isn’t easy. Here comes a well-crafted portfolio.
It can help you achieve your goals by showcasing your skills, talents, and accomplishments.
A strong portfolio sets you apart from the crowd. But how do you make one that truly stands out?
We created this guide to help you craft a compelling portfolio that highlights your unique strengths and achievements.
Choosing the Format for Your Portfolio
The first step you take is choosing the right format. Your portfolio’s format should reflect your style, the field you are entering, and the specific goals you want to achieve.
Here are some popular formats to consider:
1. Simple Presentation (PDF or PowerPoint)
A simple presentation is a versatile and easy-to-create option, ideal for showcasing different kinds of work, from writing samples to project summaries.
We also have a review article on all the ways students can use presentations. It can be a practical guide to help you present your work in the best possible way.
The presentation format is easy to share via email or print. It can be a convenient choice for students who want a straightforward way to present their skills.
Here’s how a student of the Dundee University presents their accomplishments.
2. Website
A personal website offers a dynamic and interactive way to display your portfolio. This format is perfect for students looking to make an impression in digital fields, like marketing, web development, design, or journalism.
A website can include multimedia elements like videos, interactive graphics, and downloadable files, providing a richer experience for the viewer.
Here is an example of a website created by a student, a 3d-year biology major at the University of Washington.
3. Behance
For students in creative fields such as graphic design, illustration, or photography, platforms like Behance offer a community-driven space to show your work.
Behance allows you to present your portfolio in a visually engaging way and connect with other creatives and potential employers.
Here’s a Behance portfolio of a student at the Strate School of Design (France)

4. LinkedIn
LinkedIn is an excellent option for students who want to present a professional image and connect with industry professionals. You can present your work samples, projects, and achievements adding them to your LinkedIn profile, making it accessible to potential employers and network connections.
5. GitHub
If you are a computer science student or an aspiring software developer, GitHub is a fantastic platform to display your coding projects and contributions.
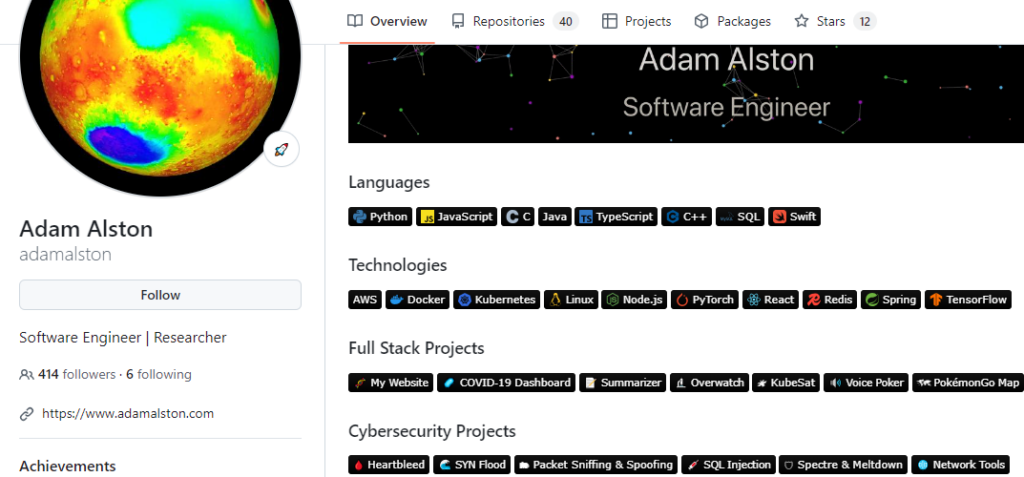
This platform allows you to share your code, collaborate with others, and demonstrate your technical skills to prospective employers, like in this portfolio of a software engineer student.
How to Choose the Right Format for Your Portfolio
When deciding on a format, ask yourself these questions:
- What field am I entering? Different industries have different expectations. For example, a graphic designer’s portfolio will look very different from that of a business student.
- Who is my audience? Consider who will be viewing your portfolio. Are you presenting to a creative director, a hiring manager, or an admissions committee? Tailor your portfolio to meet their expectations and preferences.
- What skills do I want to highlight? Think about the skills and experiences you want to showcase. A website might be best if you have multimedia projects, while a simple PDF presentation could work for more text-heavy content.
- How much content do I have? If you have a lot of content, a website or a Behance profile might be better suited to organize and display your work. For less content, a presentation or LinkedIn might suffice.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Portfolio
Now that you have a better understanding of the different portfolio formats, let’s walk through how to create a portfolio no matter the format.
Step 1: Define Your Objective
Before you start creating your portfolio, define its purpose. Are you applying for a specific job or internship? Are you presenting your work for a scholarship?
Having a clear objective will help you focus on what to include and how to present your work. Just like in the example below.

Step 2: Gather Your Work
Collect all the materials you want to include in your portfolio. This could be essays, projects, artwork, coding samples, videos, or any other work that demonstrates your skills and accomplishments.
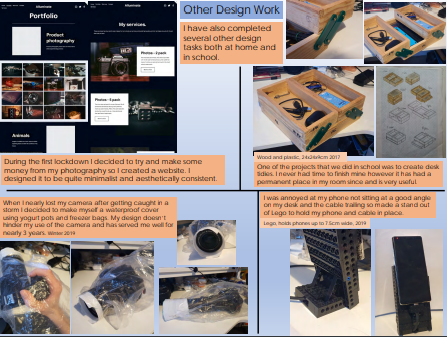
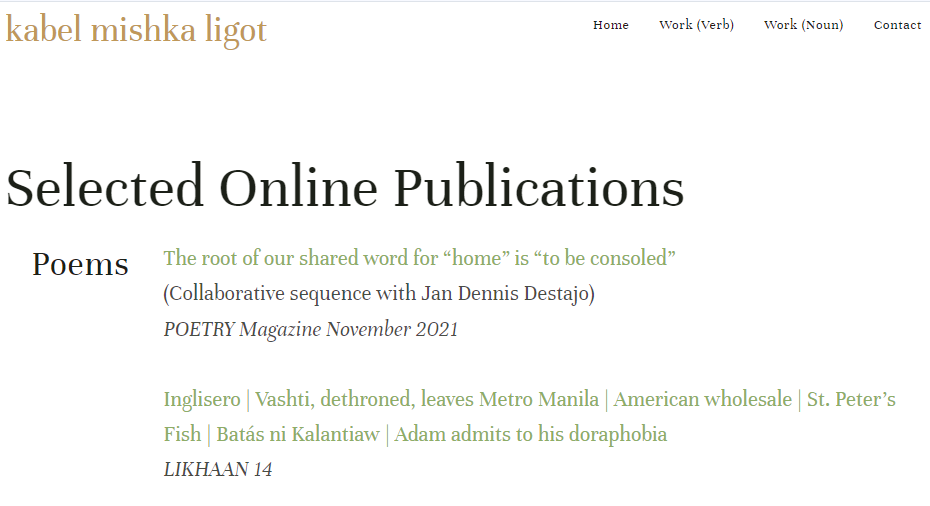
Organize your work into categories or projects to make it easier to arrange. Here’s how a student a writer from the Philippines does it.
Step 3: Choose the Design (if you opt for a presentation-style portfolio)
Select a clean and professional design that suits your field and personal style. We at Wonderslide offer a variety of designs to choose from. Look for a design that complements your work without overpowering it.
For example, this design could serve well for a Science major student.

Step 4: Create a Strong Introduction
Start your presentation with a strong introduction. Include your name, a professional photo, and a summary of who you are and what you do. This is your chance to make a great first impression, so keep it concise and engaging. Here’s how it was done by a Biology student from UW.

Step 5: Highlight Your Best Work
Dedicate each slide to a different project or piece of work. Start with your strongest examples and work your way through the rest. Include a brief description of the project, and what role you played.
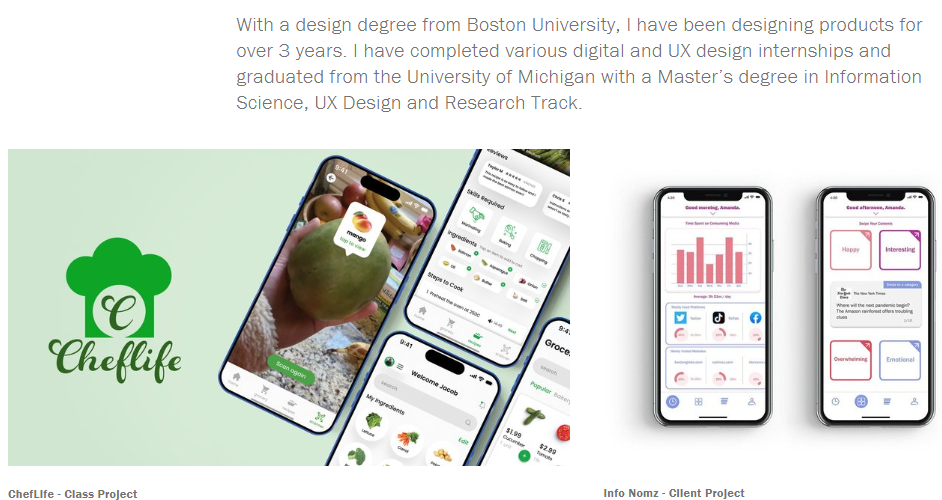
Below, you can see how a young graduate designer from Boston University presents her projects. Students can’t boast a huge portfolio, but it’s important to show your accomplishments to potential employers.
Step 6: Add Testimonials or References
If you have any testimonials from teachers, mentors, or clients, don’t be shy to add a slide for these. Positive feedback is always an incentive.
In the following example, a student studying digital marketing includes photos of happy clients and their positive feedback.

Step 7: Conclude with a Call to Action
End your presentation with a strong call to action. This could be a slide with your contact information, a link to your LinkedIn profile, or a note encouraging viewers to reach out to you for more information.
You should make it as easy as possible for potential employers or collaborators to get in touch with you, like in the example below.
Step 8: Review and Revise
Before finalizing your presentation, review it for any errors, inconsistencies, or areas that could be improved. Ask a friend, teacher, or mentor to provide feedback. Getting a second opinion always helps.
Conclusion
Creating a portfolio that stands out doesn’t have to be a huge challenge. Start by choosing the right format, then follow the steps from our guide, and you will craft a portfolio that shows your skills, accomplishments, and unique personality.
Remember, your portfolio is a reflection of you—make it count!